
The success of the internet of things and cloud services have contributed to create a need for edge computing, where data elaboration takes place at the edge of the network rather than completely on the cloud.
Edge computing may also be able to cope with limitations such as latency, limited mobile device battery life, broadband costs, security and privacy.
These are key problems in the telecommunications industry, and that is why this technology is so important for the future of the sector.
The edge computing panorama
The increase in the use of network resources is one of the most urgent challenges mobile network operators face.
In fact, over the last few years data traffic has represented a large slice of network capabilities; so many applications are based on data and services hosted in remote data centres.
This places huge pressure on the network, as data is updated and downloaded to and from mobile devices and data centres connected via the internet.
It’s plausible to think that this need will increase, above all considering increased usage of more sophisticated augmented reality devices, such as the major virtual reality headsets currently available on the market such as Oculus.
In order to keep up with increasing demand, network operators are forced to improve existing network resource capacity constantly.
So what is edge computing?
Recently Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) has been put forward as the technology that may overcome difficulties regards several situations.
The goal of edge computing is to reduce network overload, moving computing efforts from the internet to the mobile edge.
What does that mean?
In the telecommunications field, the edge node means a cell phone or a cell site.
In unusual network terms, the mobile edge is simply used as an access point, but it doesn’t analyse or elaborate user needs.
The Mobile Edge Computer technology introduces new technological elements to the mobile edge, with computational and storage abilities.
So, the new devices are distributed and co-hosted via various base station towers, which effectively work as servers.
Put simply, this technology brings basic elaboration, storage and networking physically closer to data-creating sources.
Usage applications of mobile edge computing
The introduction of MEC technology to the cellphone network permits direct execution of applications by the base station in use.
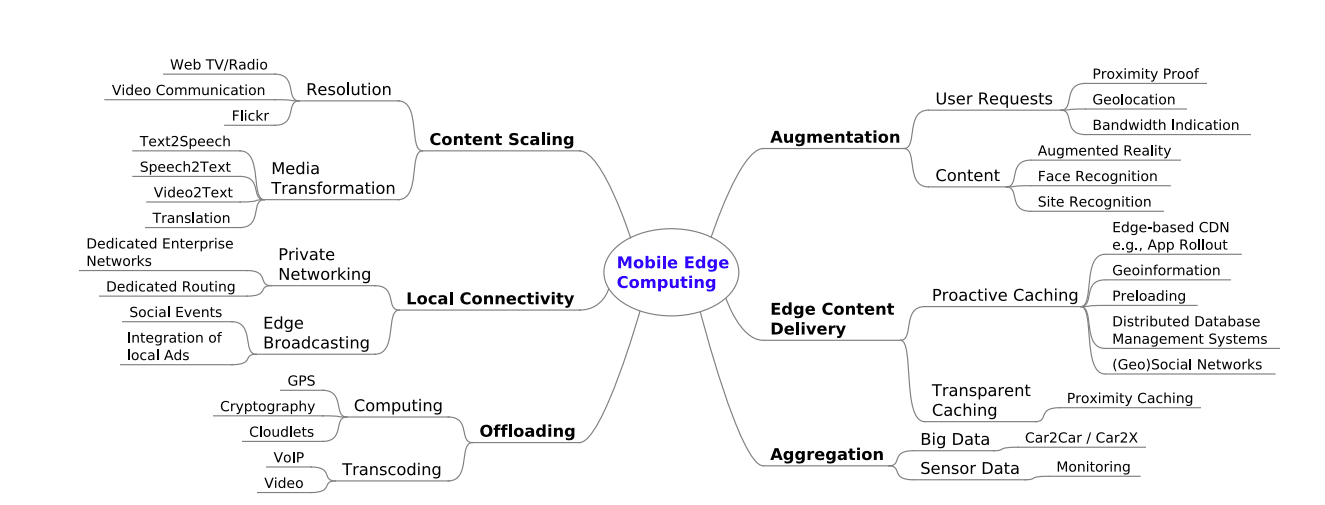
As we saw, edge computing is an IT architecture which aims to bring the applications and data closer to the users and their devices.
So it’s quite different from cloud computing, which is well-used now, and which has meant the creation of vast data centres.
Edge computing in fact means an exponential number of data centres for IT purposes.
This is why it is so important for a number of vertical sectors such as retail stores, hospitals, manufacturers and connected pilotless vehicles.
And of course, don’t forget, mobile edge computing will encourage the development of a super-efficient, fast and secure 5G network.



