Global demand for electricity is on the increase, and there is no reason to believe it will slow down. Indeed, exponential growth is forecast, whereby 2020 demand levels will be doubled by 2050.
As we know, the decarbonisation goals necessary for tackling climate change mean that we need to increase electrical energy produced by renewable sources, in particular wind and solar energy. This in turn means growth in the diffusion of energy storage systems, which play a vital role in ensuring balance between demand and supply.
It’s not by chance that investments in energy storage across the globe have already reached 3 billion dollars in 2020, and more growth is predicted for the future.
Forecasts for the future
According to forecasts by Bloomberg NEF (BNEF) published at the end of 2021, energy storage units across the world will reach a total of 358 gigawatt/1,028 gigawatt hours by the end of 2030, which is twenty times greater than the 17 gigawatt/34 gigawatt on the entire infrastructure at the end of 2020.
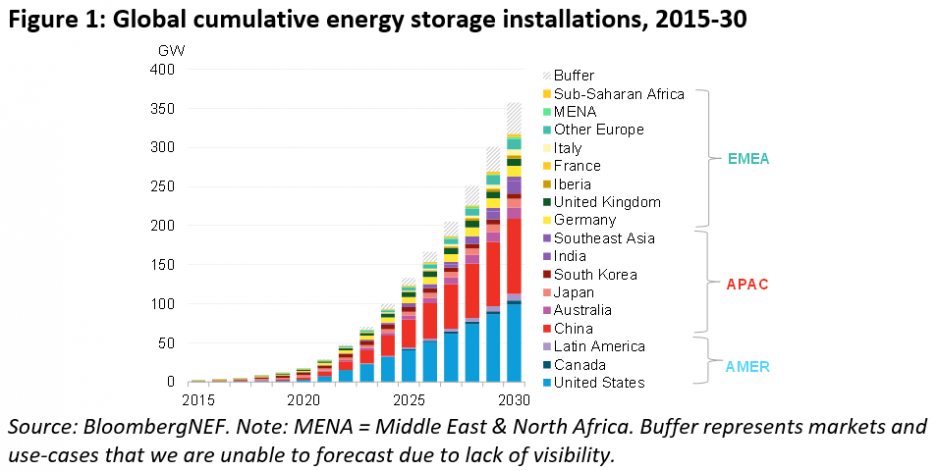
BNEF estimates that 345 gigawatt/999 gigawatt hours of new energy storage capacity will be reached globally between 2021 and 2030, that is more than Japan’s capacity for energy generation in 2020.
The USA and China are the largest markets, and will have over half of all global storage units by 2030, and more generally it will be Asia which will stimulate the sector, followed by North America.
Available storage systems
To date there is wide range of technologies regarding energy storage, which can be divided into the following five main categories:
- mechanical
- electrochemical
- compressed air
- thermal
- chemical
Rapidly evolving battery technology is driving the energy storage market, and the industry is adopting multiple lithium-ion battery chemistries. Regarding batteries, and systems that are designed around their usage, then it is electrochemical technology that is involved, which today represents a low share of the whole.
However, continuous falls in prices should allow this technology to make gains - together with hydrogen accumulators - to access a sizable market over the next 30 years.
What are the most interesting up-and-coming trends?
Regarding battery storage systems, in the near future we will see them becoming more common in the energy marketplace due to a number of relevant reasons.
Let’s take a closer look at those reasons, via analysis carried out by Deloitte, contained in this report:
- Improvement in costs and performance: particularly regarding lithium-ion batteries, for which demand is increasing due to market expansion of electrical vehicles, so costs are decreasing whilst performance is improving.
- Network modernisation: the growth in battery storage systems is in line with bringing the network up to date, including transitioning over to intelligent networks. Batteries help in exploiting the full potential of intelligent technologies and vice versa.
- Global inclination for renewables: widespread support for renewable energies and emission reductions are driving users to adopt battery storage solutions. This can increasingly be seen within the public and business sectors.
- Participation in wholesale electric markets: storing energy using batteries can also help balance the network and improve energy quality, whatever the source. Almost all the countries under analysis are renewing the structure of their wholesale market, to allow batteries to supply auxiliary energy and services.
- Financial incentives: countries such as South Korea, Italy and many other nations are increasing access to financial incentives for investment in storage. That action indicates the growing awareness of politicians regarding the range of benefits which battery storage can bring all the way through the electricity value chain.
- Elimination of FITs and of net exchanges: the reduction in feed-in tariffs (FITs) or of net payments is emerging as one of the determining factors in implementing behind-the-meter batteries in some countries, so long as clients work to get the maximum value from their roof solar panels in the absence of these incentives.
- The desire to be self-sufficient: reasons for the purchase of storage systems are not just financial ones. In Germany, for example, ecological factors, independence from public services, resilience and technical curiosity are also held to be motivating factors. Just in the same way, self-sufficiency is a strong motivational factor in Italy, the UK and Australia.
- National politics: many countries are turning to renewable energy storage to reduce their dependence on energy imports, to increase reliability and the resilience of their systems and to embrace environmental and decarbonisation goals.
As Deloitte underlines in their report “Energy storage isn't just about integrating intermittent wind and solar output: battery solutions, which can be deployed rapidly and with pinpoint precision, can be used to make the overall grid more efficient and resilient, regardless of the generation sources.”
This makes battery-based energy storage even more important, as confirmed by date from recent years’ developments and forecasts for 2030.




