Global manufacturing trends for 2024

The manufacturing sector is facing an unprecedented set of challenges and opportunities, linked to the accelerating technological evolution and global socio-economic changes.
The widespread adoption of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, coupled with growing environmental awareness and the need to address skilled labour shortages, is radically redefining the manufacturing landscape worldwide.
In this context, examining the global trends that are the driving forces behind the industry's evolution is vital to understand the dynamics at play and to identify the strategies required to maintain competitiveness and promote long-term sustainability.
In this article, we will explore a number of key trends that are shaping the future of manufacturing on a global scale. From the digitisation of factories to the transformation of supply chains, through the adoption of sustainable practices and focus on diversity and inclusion in the workplace, we will analyse how these trends are affecting the operations and strategies of manufacturing companies across the world.
1. Smart factories
Smart factories are a growing phenomenon in the global manufacturing landscape.
These facilities integrate advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), process automation, robotics and real-time connectivity to optimise operational efficiency and productivity.
Smart factories enable greater flexibility, reduce downtime, improve product quality and increase overall production capacity. They also enable more efficient resource management, helping to reduce costs and quickly adapt to market needs.
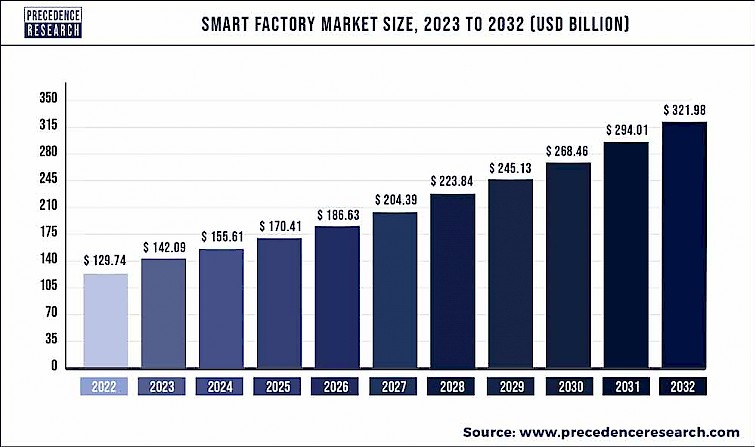
The global smart factories market size was valued at $129.74 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach approximately $321.98 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 9.52% from 2023 to 2032.
2. AI, machine learning and advanced analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning and advanced analytics are radically transforming the manufacturing sector, enabling companies to collect and analyse vast amounts of data to make more informed decisions.
These technologies support demand forecasting, optimise the supply chain, improve production accuracy and enable predictive maintenance.
The adoption of AI and machine learning-based systems allows companies to continuously improve operations, increase efficiency and maintain a competitive advantage in the global market.
According to a Deloitte survey, the manufacturing sector stands out as the leading sector in terms of data generation. This indicates a significant volume of data generated.
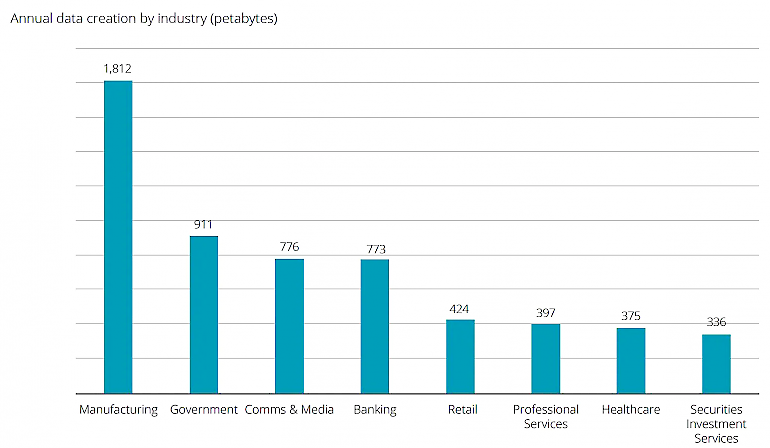
Manufacturers could therefore adopt AI, machine learning and data analysis tools to make the very best use of that data.
3. Predictive maintenance and digital twin technology
Predictive maintenance, enabled by digital twin technology, has become a fundamental pillar of modern manufacturing plant management.
Digital twins are digital models that replicate the conditions and functioning of physical assets in real time, allowing operators to monitor performance, predict failures and proactively plan maintenance interventions.
This approach reduces maintenance costs, minimises downtime and extends plant life, ensuring its continuous and reliable production.
Indeed, predictive maintenance may result in a 40% reduction in maintenance costs, a 70% decrease in downtime and a 25-30% increase in overall equipment effectiveness.
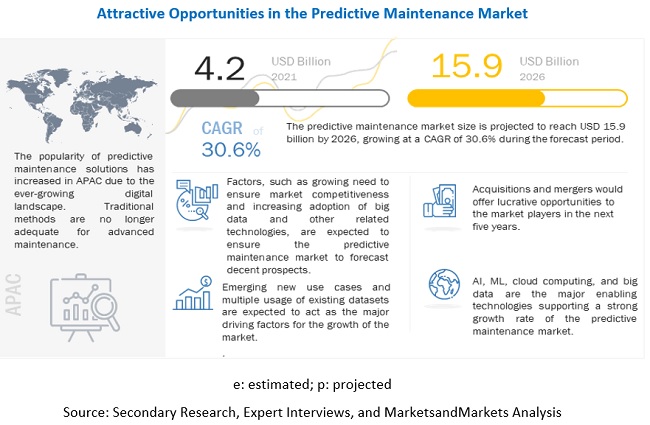
The predictive maintenance market size is expected to reach $15.9 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 30.6%.
4. Supply chain restructuring
Supply chain restructuring is another significant trend in the global manufacturing landscape, driven by the need to reduce risk and increase resilience, particularly in the aftermath of the difficulties generated first by the pandemic and then by the war in Ukraine.
Companies are redesigning their supply chains to reduce dependence on single suppliers or geographic regions, to diversify supply sources and to implement digital technologies so that they can improve visibility and traceability across the entire value chain.
This restructuring process is essential to mitigate the impacts of unexpected disruptions, such as health crises or natural disasters, and ensure the continuity of operations.
5. Microfactories
Microfactories are emerging as an innovative solution to meet the growing demand for local and customised production.
These facilities, characterised by their small size and high level of automation, enable small-scale production, reducing transport costs, delivery times and the risk of overproduction.
Microfactories foster flexibility and product customisation, allowing companies to adapt quickly to market needs and consumer preferences.
6. Wages and new career paths
According to Randstad, 62% of workers worldwide consider salary the number one factor in joining or leaving a company. This has led many manufacturers to increase wages to meet this demand.
In addition, companies are also facing a growing shortage of skilled labour, so they are adopting various strategies to attract and retain workers.
These strategies include increasing wages, offering additional benefits, and training and retraining programmes to acquire the skills necessary in the context of digital transformation.
Investing in human capital has become crucial to ensure a skilled and motivated workforce, which is vital in maintaining high production standards and business competitiveness.
7. Diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) initiatives
DEI initiatives are gaining increasing importance in the manufacturing sector as companies recognise the benefits of a diverse and inclusive workforce.
Promoting diversity in terms of gender, ethnicity, background and skills not only fosters a more equitable and respectful work environment, but also stimulates innovation, improves market representativeness and enhances corporate reputation.
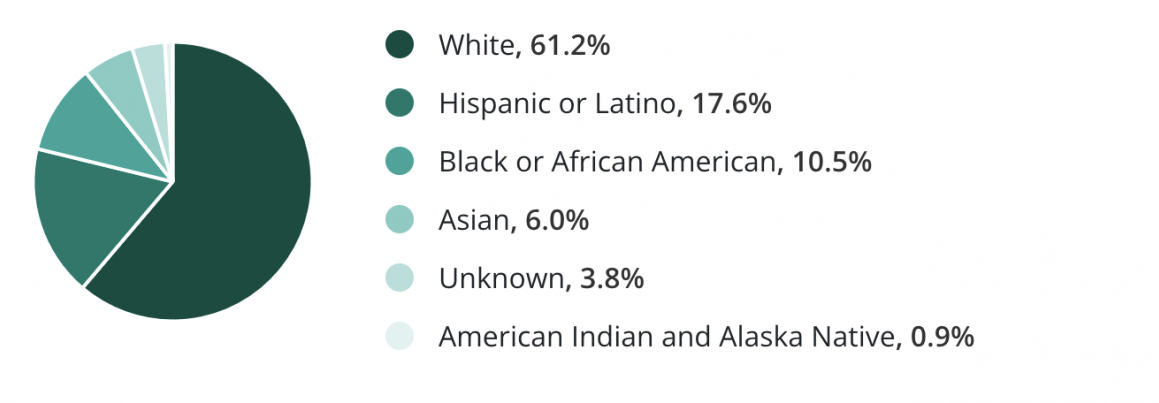
Currently, the most common ethnicity among manufacturing workers is white, making up 61.2% of all manufacturing workers. In comparison, 17.6% of manufacturing workers are Hispanic or Latino and 10.5% of manufacturing workers are Black or African American (Zippia).
Regarding gender, just 32% of human resources are female.
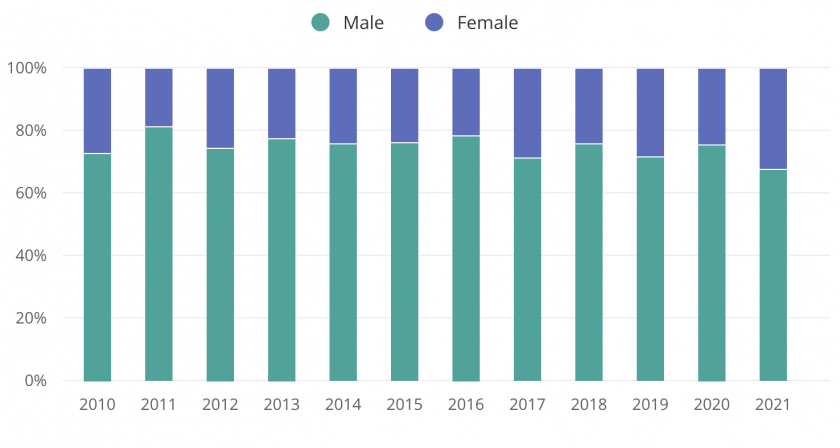
According to the AEM - Association of Equipment Manufacturers, research and data speak clearly for themselves: a diverse work environment is more innovative, more creative and better at decision-making and problem-solving. More importantly, diversity leads to a lower employee turnover rate, better hiring results, engaged employees and, ultimately, a more respectable organisation.
For these reasons, companies are adopting targeted policies and programmes to promote diversity, equity and inclusion within their workforces.
8. Carbon Neutrality
One fifth of the world's carbon emissions comes from the manufacturing and production sectors, which consume 54% of the world's energy sources, according to the World Economic Forum.
Carbon neutrality has therefore become a primary goal for those manufacturers committed to fighting climate change.
Reducing carbon emissions through the adoption of sustainable technologies, optimising production processes and transitioning to renewable energy sources is key to limiting the environmental impact of manufacturing operations.
Companies are implementing practices and policies to reduce their carbon footprint, thus contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change and promote environmental sustainability.
Conclusions
In light of the above, it becomes evident that the manufacturing landscape is undergoing an unprecedented period of transformation, characterised by complex challenges and significant growth opportunities.
Only by embracing change and adopting a future-oriented mindset can companies hope to remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic and global environment.



